Each day, countless vehicles travel from one place to another across the world, ultimately ending up in a parking area. In today’s urban environments, where there are large numbers of cars and limited parking availability, managing these spaces efficiently has become essential. City planners now see parking management as an important aspect of public service, aiming to ensure that residents remain satisfied and visitors feel welcomed.
“We can easily manage if we will only take, each day, the burden appointed to it. But the load will be too heavy for us if we carry yesterday’s burden over again today, and then add the burden of the morrow before we are required to bear it factorial non.” Delbart
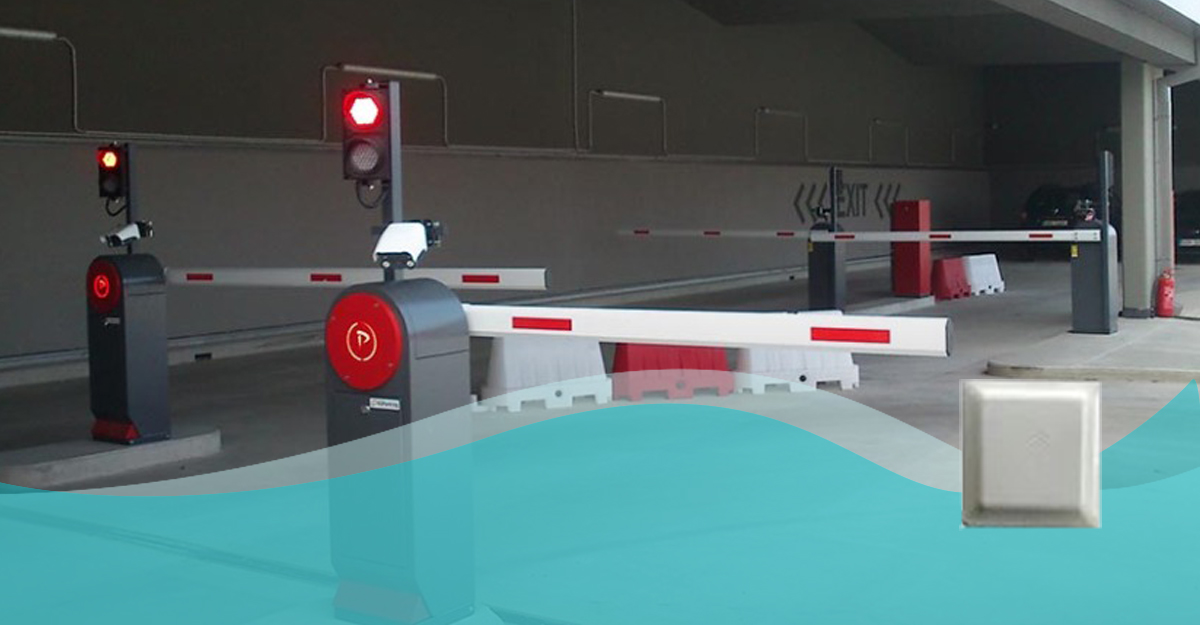
Parking also serves as a frontline in securing a restricted perimeter with a fence and barrier in some areas. The mechanism used to identify, authenticate, and allow access is frequently the weakest point of a physical barrier to prevent unauthorized vehicles from entering an area.
Although various technologies like license plate recognition, barcode scanners, and radio-controlled switches are used, RFID stands out as a solution that combines physical security—through barriers—with the digital protection needed to prevent unauthorized entry.
RFID tags provide:
“A unique, non-duplicable identifier stored in user memory and placed in a discreet, unobtrusive location on the vehicle.”
RFID Readers provide:
Detection that is both quick and long-range Adaptability to existing access control panels — (Weigand, Serial, Ethernet, WLAN) Installation is simple. Accurate and dependable performance
What Exactly Is RFID?
RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a wireless technology used to identify and track objects using radio waves. It involves three main components: an RFID tag, a reader, and an antenna. The RFID tag contains a microchip that stores data and an antenna that transmits this information. When the reader sends out a radio signal, the tag responds by sending back its stored data, allowing the object it’s attached to be identified. RFID tags can be passive (without a battery, powered by the reader’s signal) or active (with a battery for longer range).
What Are UHF Reader Systems?
UHF Reader Systems are a type of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology that operate in the Ultra High Frequency (UHF) range, typically between 300 MHz to 3 GHz, with most RFID UHF systems using the 860–960 MHz band (depending on regional regulations).
A UHF reader system consists of:
- UHF Reader – A device that emits radio waves to communicate with RFID tags.
- Antenna – Transmits and receives signals between the reader and the tags.
- UHF RFID Tags – Small electronic devices attached to objects, which store data and respond to the reader’s signal.
- Software/Database – Processes the data collected by the reader.


